Green hydrogen production projects are on the rise in Portugal. At the beginning of the year, the Government announced the signing of 25 business proposals – 21 green hydrogen projects and four biomethane projects – involving total funds to the amount of 102 million euros from the Portuguese Recovery and Resilience Plan, which will give rise to a reduction of 167,000 tons of carbon dioxide emissions. Furthermore, the country has five planned “hydrogen valleys”, which include the entire green hydrogen value chain, from production to storage and distribution. Eighty of these projects are planned worldwide, which, when fully operational, will represent future production of 8.5 million tons.
One of the aims is to meet the goals of the National Hydrogen Plan for 2030, including the injection of 10% to 15% of green hydrogen into natural gas networks and the creation of 50 to 100 service stations to supply this fuel, representing a total of 1.5% to 2% of final energy consumption.
Galp has been increasingly involved in this commitment, and in September announced the construction of a 100-MW electrolyser designed to produce up to 15,000 tons of renewable hydrogen a year. The inclusion of this large-scale project in the operations of the Sines refinery will also enable the company to replace around 20% of current grey hydrogen consumption and could result in a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions of around 110,000 tons a year. These new units are expected to commence operations in 2025. As far as Paula Amorim, the company´s chair, is concerned, this initiative, along with others underway, places Galp “at the forefront of the development of low-carbon solutions essential to ensuring energy transition”.
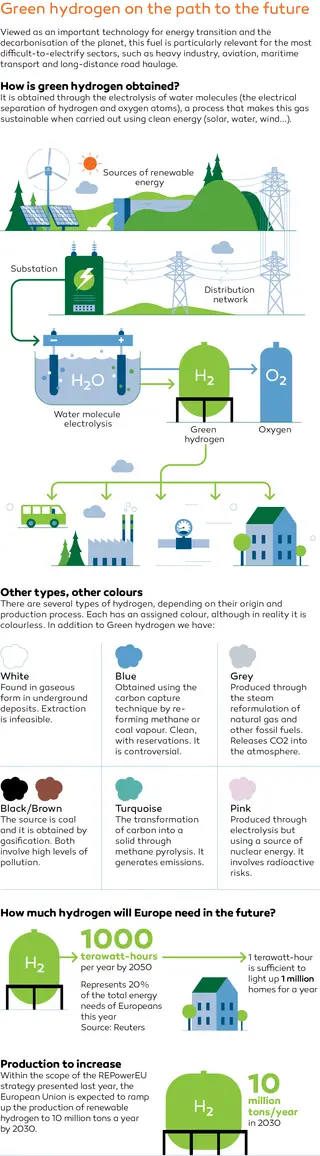
The infographic below illustrates how green hydrogen is obtained and the differences when compared to other types of hydrogen.